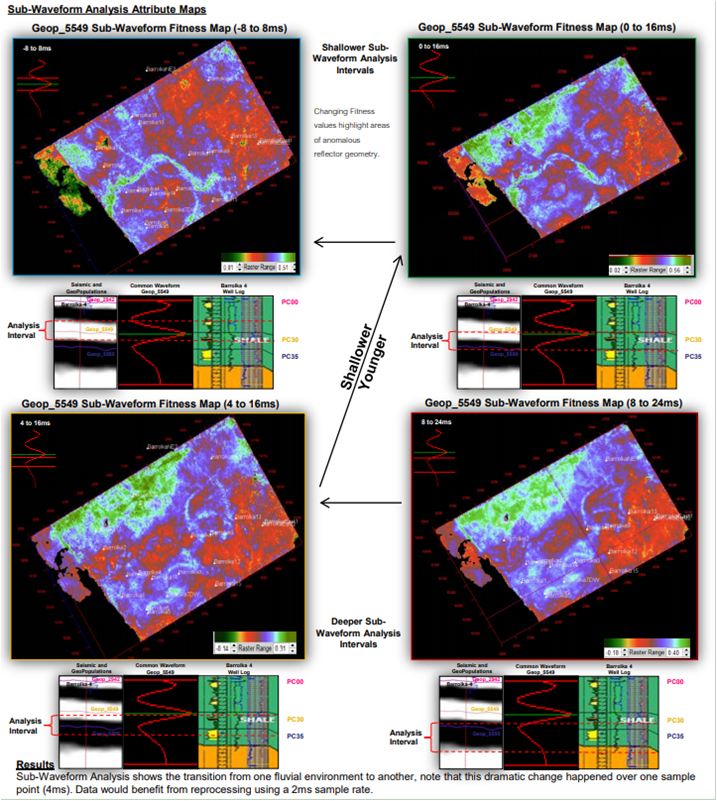

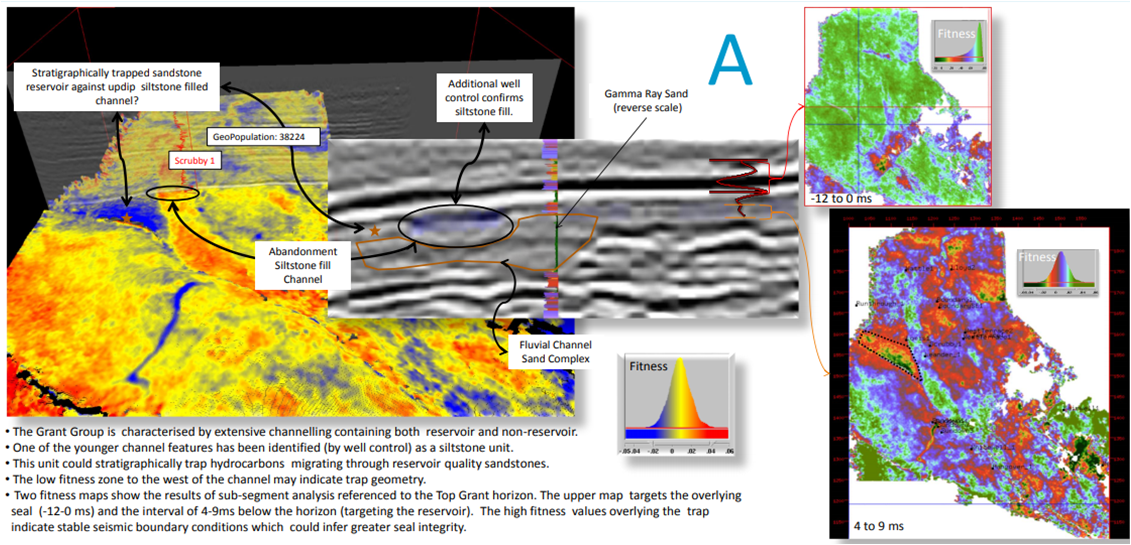
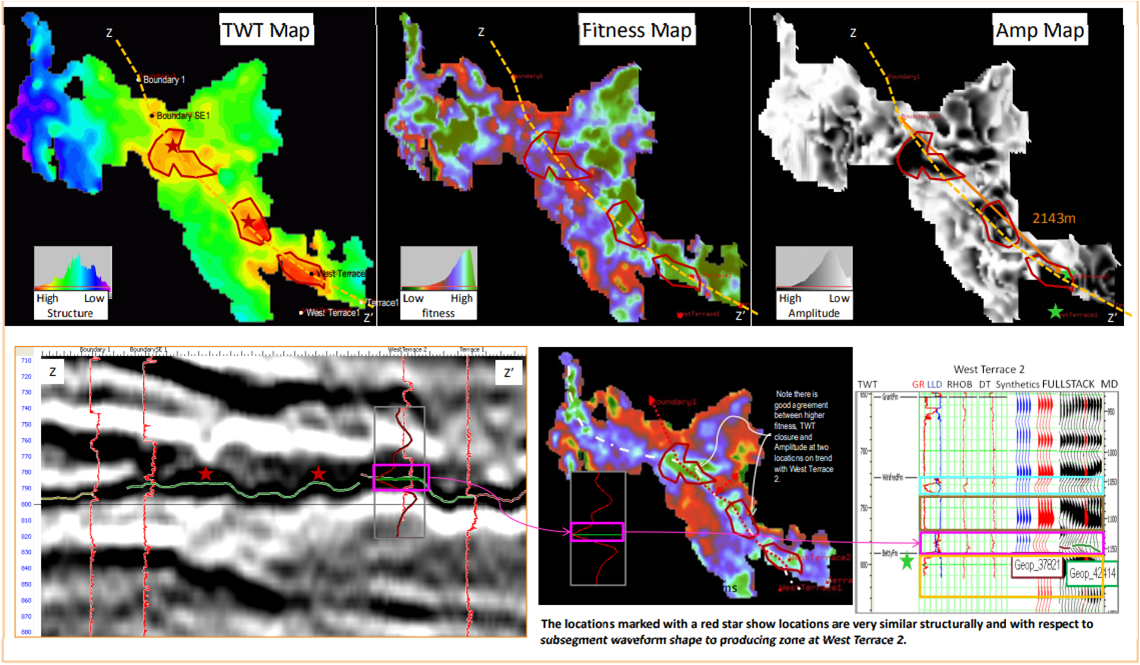
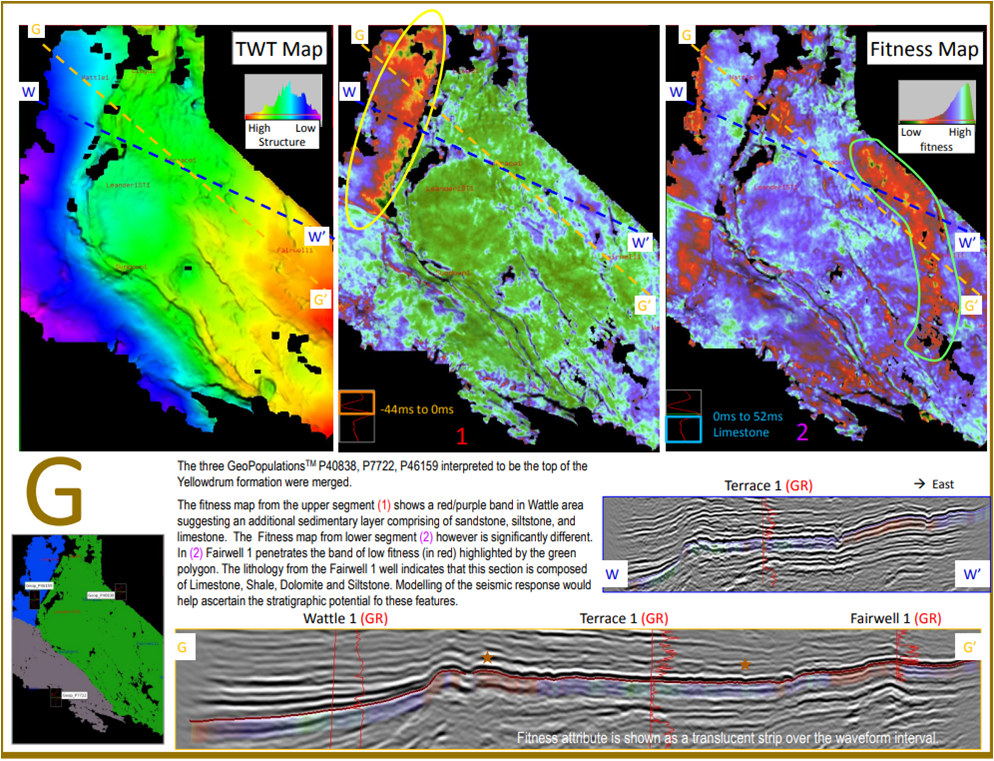
The observation of the GeoPopulation database revealed many new insights and opportunities, amongst them:
Cooper-Eromanga Basin, SW Queensland (Australia)
Permian, Fluvial channel sands PC30 and PC35